Tofacitinib's Role in Granuloma Annulare Treatment

Overview of Research Topic
Granuloma annulare is a benign yet often perplexing inflammatory skin disorder characterized by raised, reddish or skin-colored bumps. Its etiology is not fully understood, leading to challenges in its management. This skin condition commonly affects children and young adults, presenting itself in various forms, including localized and generalized types. With the increasing incidence of autoimmune disorders, understanding granuloma annulare has gained importance.
Tofacitinib, a Janus kinase inhibitor, has emerged as a potential treatment option for several inflammatory conditions. Its role in modulating immune responses makes it a compelling candidate for managing granuloma annulare. This article examines the intersection of tofacitinib and granuloma annulare, aiming to unpack the nuances of its effectiveness, mechanisms, and safety profile.
Brief Background and Context
The interest in granuloma annulare has risen significantly in recent years. Historically, treatment options have been limited and largely ineffective. The introduction of tofacitinib offers a fresh perspective. Its ability to inhibit Janus kinase pathways could potentially down-regulate the inflammatory processes associated with granuloma annulare. By analyzing current research and case studies on tofacitinib’s impact, we aim to contribute to a growing body of literature that seeks to clarify the interactions between immune-modulating medications and skin disorders.
Importance in Current Scientific Landscape
Understanding the therapeutic potential of tofacitinib in granuloma annulare is essential in the current scientific landscape. As more clinicians and researchers explore novel treatment pathways, this study underscores the need for comprehensive analysis and clinical trials. Insights gained here could facilitate improved patient outcomes and reshape management strategies for this benign skin entity.
Methodology
An in-depth analysis of the relationship between tofacitinib and granuloma annulare requires a structured approach to methodology.
Research Design and Approach
The research adopts a qualitative design, focusing on an extensive review of current literature, clinical trials, and case reports. This methodology enables a nuanced understanding of the potential of tofacitinib in treating granuloma annulare. By synthesizing qualitative findings, the research identifies patterns and gaps that are crucial in establishing treatment protocols.
Data Collection Techniques
For this analysis, we employed several data collection techniques, including:
- Systematic literature review: To identify relevant studies that detail the outcomes of tofacitinib use in patients with granuloma annulare.
- Case studies analysis: Reviewing documented cases where tofacitinib has been utilized to understand practical implications and real-world outcomes.
- Expert interviews: Engaging with dermatologists and rheumatologists to gather insights on the clinical experience with tofacitinib in inflammatory skin disorders.
This methodical approach provides a solid foundation for our findings and discussions, aiming to illuminate the potential role of tofacitinib in managing granuloma annulare.
"Tofacitinib represents a beacon of hope for patients with granuloma annulare who have not responded to conventional therapies."
With that said, the following sections will further delve into clinical presentation, treatment options, safety profiles, and the specific mechanisms by which tofacitinib may exert its therapeutic effects in the context of granuloma annulare.
Prelude to Tofacitinib
Tofacitinib is a significant therapeutic agent, particularly for conditions like autoimmune diseases. As a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, it functions by targeting specific pathways that are critical in the inflammatory process. It offers distinct advantages over traditional therapies, such as faster onset of action and oral administration. Understanding tofacitinib is essential when discussing its role in various inflammatory conditions, including granuloma annulare.
Mechanism of Action
Tofacitinib operates by inhibiting the Janus kinase enzymes, primarily JAK1 and JAK3. These enzymes play a crucial role in the signaling pathways of various cytokines involved in immune response. The inhibition of JAK pathways leads to a reduction in inflammatory mediators, which can help manage disorders characterized by excessive inflammation. In simpler terms, by blocking these pathways, tofacitinib can lessen the severity of inflammation in affected tissues, providing symptomatic relief for patients suffering from related conditions.
Approved Indications
Tofacitinib is notably approved for several autoimmune diseases. These include rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ulcerative colitis. The advancement into treating granuloma annulare, though not yet officially approved, shows promise in clinical research. This emerging perspective on tofacitinib highlights its versatility and potential for broader applications, particularly for patients with granuloma annulare who do not respond well to conventional treatments.
Overview of Granuloma Annulare
Granuloma annulare is necessary to understand in the context of tofacitinib's role in treatment. This skin disorder is generally benign but can be confusing and frustrating for patients due to its sometimes persistent nature. Addressing granuloma annulare comprehensively helps in grasping why a medication like tofacitinib can be a potential treatment option.
Etiology and Pathophysiology
The etiology of granuloma annulare is not fully understood. Some studies suggest autoimmune mechanisms contribute to its development. External factors, such as infections, medications, or trauma to the skin, may trigger the condition in predisposed individuals. Histologically, granuloma annulare is characterized by the presence of dense aggregates of macrophages, which resemble giant cells, within the dermis. These findings are typical in inflammatory conditions of the skin, indicating an underlying immune response that can be mismanaged in afflicted patients. Most commonly, granuloma annulare occurs in children and young adults, underscoring the need for effective management options as it may affect their quality of life.
Clinical Presentation
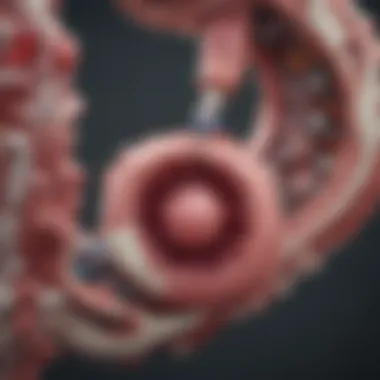

Clinically, granuloma annulare presents as raised, reddish bumps or lesions, often forming rings or annular shapes. The lesions are usually painless and can vary in size. They may take weeks to months to resolve spontaneously. While the skin findings are often the most visible signs, systemic symptoms are generally absent, which can lead some to dismiss the impact of the condition. The lesions primarily appear on the hands and feet, but they can also involve other areas. This presentation can lead to confusion with other dermatologic disorders, making diagnosis a critical aspect of patient management.
Subtypes of Granuloma Annulare
Granuloma annulare is not a uniform condition; it can manifest in several forms. The most common subtype is localized granuloma annulare, presenting isolated lesions. Generalized granuloma annulare showcases widespread lesions across the body. Subcutaneous granuloma annulare might develop deeper in the dermis, presenting as nodular lesions. Lastly, persistent granuloma annulare can resist treatment, leading to chronic problems for some individuals. Distinguishing these subtypes is crucial as it influences treatment decisions and expectations for both healthcare providers and patients.
Understanding these nuances is essential for any potential interventions, including those involving tofacitinib. By analyzing the characteristics and complexities of granuloma annulare, this article can provide insight into how tofacitinib may bring value to patient outcomes.
Treatment Options for Granuloma Annulare
Understanding the treatment options for granuloma annulare is crucial. Patients dealing with this condition often seek relief from its symptoms, which can include skin lesions and discomfort. This section will explore two primary categories of treatment: topical treatments and systemic treatments. Each has its own set of benefits and considerations that can influence patient management and outcomes.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments serve as a first-line approach for many patients with granuloma annulare. These treatments aim to target the lesions directly, potentially reducing inflammation and promoting healing. Common topical options include corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors, both of which have shown efficacy in managing localized forms of the condition.
- Corticosteroids: These are among the most frequently prescribed topical agents. They work by suppressing the inflammatory response. Potent corticosteroids may be necessary for more significant lesions. However, prolonged use can lead to skin thinning and other side effects.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Drugs like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus are often utilized as alternatives to corticosteroids, especially in sensitive areas like the face. They reduce inflammation without the adverse effects associated with long-term corticosteroid use.
Topical treatments are often preferred due to their localized effects and lower risk of systemic side effects. However, they may not be sufficient for more extensive or resistant cases.
In applying topical treatments, adherence to a consistent routine is vital. Patients must follow the application instructions provided by their healthcare providers. Moreover, it is important to monitor any changes in the skin and report these to the treating physician for timely adjustments to the treatment plan.
Systemic Treatments
Systemic treatments are typically considered for patients with more extensive granuloma annulare or those who do not respond to topical therapies. These options can address the condition from a broader perspective through oral or injected medications. Below are key systemic treatments utilized in the management of granuloma annulare:
- Corticosteroids (Oral): Systemic corticosteroids can be effective, especially for severe or widespread lesions. They rapidly reduce inflammation but require careful monitoring due to potential side effects such as weight gain, blood sugar changes, and increased risk of infection.
- Immunosuppressants: Agents such as methotrexate or azathioprine may be employed for patients who do not respond adequately to corticosteroids alone. These medications dampen the immune response, helping to control the inflammatory processes involved in granuloma annulare.
- Janus Kinase Inhibitors: Emerging evidence suggests that tofacitinib, a Janus kinase inhibitor, could play a role in managing granuloma annulare. By targeting specific pathways involved in inflammation, it may offer a novel therapeutic avenue, especially for patients with resistant forms of the disease.
- Biologics: While still under investigation, biologic therapies may also hold promise for granuloma annulare. These medications typically target specific components of the immune system, offering alternatives for patients who may not achieve success with conventional systemic options.
Tofacitinib in the Context of Granuloma Annulare
Tofacitinib is a Janus kinase inhibitor that has gained attention for its potential application in treating various immune-mediated diseases. Granuloma annulare, a chronic inflammatory skin condition, has limited treatment options, which makes the exploration of tofacitinib's role in this context particularly relevant. By examining how tofacitinib interacts with the pathophysiology of granuloma annulare, we can gain insights into its therapeutic benefits as well as its limitations. Its mechanisms of action can lead to a deeper understanding of inflammation regulation in skin disorders, which is crucial for advancing treatment strategies.
Efficacy Evidence
The efficacy of tofacitinib in treating granuloma annulare has been a subject of emerging research. Clinical studies have begun to illustrate its therapeutic potential. Although large scale, controlled trials are still necessary, some preliminary findings suggest that tofacitinib may help in reducing the lesions associated with granuloma annulare.
In various case reports, patients have shown notable improvements in their skin condition after beginning treatment with tofacitinib. Symptoms such as inflammation and itching were significantly alleviated. However, most of these observations were made in small cohorts, emphasizing the need for further large studies.
Additionally, understanding the specific biomarkers that may predict a positive response to tofacitinib can enhance its use in clinical settings. Patients seeking therapies that improve both the cosmetic and symptomatic aspects of granuloma annulare may find tofacitinib to be a compelling option despite current evidence still being limited.
Mechanistic Insights
Tofacitinib functions by inhibiting the Janus kinase pathways, which play a crucial role in the signaling of various cytokines involved in the inflammatory process. Granuloma annulare reflects an underlying dysregulation of immune responses, where proinflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and IL-17 have been implicated. By interrupting these signaling pathways, tofacitinib potentially resets the immune response.
Mechanistically, this targeting could reduce the inflammatory milieu associated with granuloma annulare lesions. Furthermore, it may contribute to reducing the progression of the disease by inhibiting the factors that drive chronic inflammation. Understanding these mechanisms provides a foundation for evaluating both the clinical and biological implications of using tofacitinib in this specific context.
"Tofacitinib offers a novel approach that departs from traditional therapies by directly intervening in the inflammatory response."
Safety and Side Effects of Tofacitinib
Understanding the safety and side effects of tofacitinib is crucial within the scope of this article. Though this medication shows promise in treating granuloma annulare, its safety profile cannot be overlooked. Patients and healthcare providers alike must navigate the complexities of its potential adverse effects. Knowing the risks allows for better management and informed decision-making in clinical practice.
Common and Serious Adverse Effects
Tofacitinib is known to cause several common and serious adverse effects. Understanding these effects is important for both patients and practitioners.


- Common Adverse Effects: Some frequent effects that patients may experience include:
- Serious Adverse Effects: There are also severe risks associated with tofacitinib. These include:
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Potential for headache
- Liver enzyme elevations
- Risk of thrombosis, such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism
- Serious infections, which can lead to hospitalization
- Elevated cholesterol levels, requiring monitoring
Recognizing these effects early can be essential in maintaining patient safety during treatment.
Monitoring and Management of Risks
Monitoring and managing risks associated with tofacitinib is pivotal. Proper protocols can mitigate potential complications. Consider the following strategies:
- Regular Monitoring: Patients should undergo routine blood tests to monitor liver function, blood cell counts, and cholesterol levels. This helps to identify any abnormalities early.
- Infection Screening: Screening for infections prior to and during therapy is advisable. Patients should be educated about signs of infections to report timely.
- Lifestyle Considerations: Health practitioners might suggest lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, to combat side effects like elevated cholesterol.
The importance of a holistic approach to monitoring and management cannot be understated. As a fine balance between efficacy and safety must be maintained, ongoing dialogue between patient and provider is essential for optimal outcomes.
Case Studies Involving Tofacitinib and Granuloma Annulare
The exploration of case studies involving tofacitinib and granuloma annulare enriches understanding of how this treatment approaches the complexities of the condition. They provide real-life, evidence-based insights that can be vital to clinicians and patients alike. Each case study offers a unique perspective on both the efficacy of tofacitinib and its versatility as a treatment option. These narratives bridge the gap between theoretical research and practical application, which are crucial for making informed treatment decisions.
Successful Outcomes
Several documented cases illustrate remarkable responses to tofacitinib in patients suffering from granuloma annulare. These successes often highlight significant improvements in skin lesions and associated symptoms.
- Noteworthy Case 1: A 35-year-old female patient with disseminated granuloma annulare showed impressive clearance of lesions after initiating treatment with tofacitinib. Over a period of 12 weeks, her skin revealed substantial healing, allowing for a better quality of life.
- Noteworthy Case 2: In another instance, a 50-year-old male who experienced both localized and papular forms exhibited near-complete resolution within three months. The physician noted a decrease in inflammation markers, further supporting the treatment’s effectiveness.
In both cases, tofacitinib not only mitigated symptoms but also positively impacted patients' mental well-being, as visible skin improvements often correlate with enhanced self-esteem. The successful outcomes underline the potential benefits of tofacitinib as a feasible approach for managing granuloma annulare.
Failures and Complications
Nonetheless, not all case outcomes are favorable. Some patients exhibit limited response or complications as a result of tofacitinib treatment.
- Noteworthy Case 1: One patient, a 40-year-old male, experienced exacerbation of skin lesions after six weeks of treatment. The increase in lesions led to discontinuation of the therapy, highlighting the variable response among patients.
- Noteworthy Case 2: Another example involved a 30-year-old female who developed serious gastrointestinal side effects during her course of tofacitinib treatment. This complication necessitated an alternative medication strategy, bringing to light the importance of monitoring side effects.
Comparative Effectiveness of Tofacitinib
The topic of comparative effectiveness is vital in the context of tofacitinib and its relatively newer position in the treatment landscape. Tofacitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, which has been used primarily for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ulcerative colitis. Its potential application in granuloma annulare establishes a need for evaluating its effectiveness against traditional therapies. In essence, this section aims to clarify how tofacitinib stands in comparison to established treatments for this benign inflammatory skin disorder.
Tofacitinib vs Traditional Therapies
Traditional therapies for granuloma annulare, such as topical corticosteroids and intralesional injections, have been widely researched and are generally considered standard management.
- Topical Corticosteroids: These agents remain the first-line treatment. They reduce inflammation, but the effectiveness can vary, and long-term use may lead to skin thinning and other side effects.
- Intralesional Corticosteroids: Injection directly into the lesions can provide targeted relief, although it may not be feasible for widespread lesions.
- Systemic Therapies: Medications like methotrexate or azathioprine have been employed, but they carry the risk of significant side effects, and their effectiveness is not guaranteed in every patient.
In contrast, tofacitinib's mechanism as a JAK inhibitor presents an innovative option. Early studies show that tofacitinib may provide a quicker response in reducing lesions compared to these traditional therapies. The oral administration of the drug is also more convenient for many patients.
Tofacitinib in Clinical Trial Contexts
In clinical trial contexts, tofacitinib's performance is increasingly analyzed. Recent studies aimed to assess its safety and effectiveness specifically for granuloma annulare. Parameters such as lesion size reduction, the number of lesions, and patient-reported outcomes are often measured.
"Tofacitinib offers a unique approach by modulating immune response pathways, which traditional therapies do not address to the same extent."
Preliminary results indicate that participants receiving tofacitinib often experience significant improvements, particularly in severe cases that did not respond to conventional methods. Furthermore, the need for more large-scale trials exists to solidify these findings and investigate long-term outcomes.
By examining tofacitinib in direct comparison to established treatments through rigorous clinical trials, a clearer understanding emerges regarding its effectiveness and overall patient benefit. This invites further exploration into whether tofacitinib may become a new standard in the treatment protocol for granuloma annulare, especially for patients who resist typical therapies.


Regulatory Perspectives and Guidelines
Regulatory perspectives and guidelines play a crucial role in the management of healthcare treatments, especially in the context of new medications like tofacitinib. Understanding how regulatory bodies evaluate and approve these treatments can have significant implications for clinicians, researchers, and patients. This section explores the stances of major regulatory agencies and clinical practice recommendations concerning the use of tofacitinib for granuloma annulare.
FDA and EMA Stances
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) are two pivotal regulatory bodies that oversee the approval and monitoring of medical treatments. Both organizations have established frameworks for assessing the safety and efficacy of drugs before they become available to the public.
Tofacitinib, known as a Janus kinase inhibitor, received its initial FDA approval for treating conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. The FDA emphasizes the need for robust clinical trials to determine the drug's risk-benefit profile. In turn, these trials must include diverse populations, ensuring that the findings are applicable to a broader patient demographic.
The EMA evaluates drugs similarly but often engages in a dialogue with healthcare providers and patient groups during assessment. They focus on long-term outcomes and how treatments impact quality of life in patients with chronic conditions. For instance, there is an increased interest regarding tofacitinib’s applicability to granuloma annulare and its potential benefits as a novel therapy in managing this condition.
Clinical Practice Recommendations
Guidelines developed by organizations such as the American Academy of Dermatology provide clinical practice recommendations for healthcare professionals. These guidelines often include the following points regarding tofacitinib:
- Indication for Use: While traditionally focusing on auto-immune conditions, tofacitinib is now considered for granuloma annulare following anecdotal evidence and early clinical studies showing positive outcomes.
- Dosing Considerations: The recommended dosage may differ based on patient characteristics, such as previous treatments and the severity of granuloma annulare. Healthcare providers should customize the treatment plan based on individual responses.
- Monitoring Recommendations: Regular monitoring for adverse effects is critical, especially considering the drug's side effect profile outlined by the FDA. Clinicians are encouraged to monitor blood counts and liver function tests periodically.
Clinical guidelines are vital tools that inform practitioners about best practices to optimize patient care.
Overall, understanding regulatory perspectives and adhering to clinical practice guidelines ensures that treatments like tofacitinib are used effectively and safely in managing granuloma annulare.
Future Directions in Research
Researching the future of tofacitinib in relation to granuloma annulare is vital. This area needs exploration for several reasons. First, the existing studies show promise, but they are not exhaustive. There is a clear opportunity to analyze the long-term impact and effectiveness of tofacitinib on granuloma annulare. Most notably, understanding how this drug could offer solutions where traditional treatments have failed is essential. The insights gathered from future research can guide clinicians in making informed choices about therapy options.
Novel Therapeutic Approaches
Innovative therapeutic strategies must be identified and explored for granuloma annulare that may enhance the utility of tofacitinib. Research may investigate combination therapies involving tofacitinib and other agents. For example, using tofacitinib alongside corticosteroids or other immunomodulators may produce superior outcomes. There is also potential in evaluating topical formulations of tofacitinib. This could address localized manifestations more effectively, potentially leading to fewer systemic side effects.
Selective inhibitors targeting specific pathways in granuloma annulare could be combined with tofacitinib to refine treatment. A deeper understanding of the pathophysiology offers a chance for personalized medicine approaches, where treatments are tailored to individual patient profiles.
Longitudinal Studies and Outcomes
Longitudinal studies will provide critical insights into the lasting effects of using tofacitinib for granuloma annulare. These studies should track patient outcomes over time, assessing both effectiveness and safety. By analyzing data over multiple years, researchers can develop a better understanding of how chronic use impacts skin health and overall quality of life. It is also important to monitor the development of any long-term complications or adverse effects associated with prolonged tofacitinib therapy.
Additionally, these studies could help establish biomarkers for response. Identifying patients who are likely to benefit most from tofacitinib could optimize treatment outcomes.
To summarize, research should focus on novel therapeutic combinations and long-term patient outcomes. These efforts could enhance our understanding of tofacitinib and develop more effective treatment strategies for granuloma annulare.
Closure
The conclusion wraps up the comprehensive examination of tofacitinib in the context of granuloma annulare. It is essential to underscore the key insights gained throughout the article. Tofacitinib is positioned as a potential therapeutic option for granuloma annulare, a skin disorder characterized by benign inflammation. Its mechanism as a Janus kinase inhibitor suggests a direct influence on inflammatory pathways, offering relief to affected patients.
In summary, the implications of the findings discussed here are meaningful for various stakeholders in the medical field. For clinicians, understanding the efficacy of tofacitinib can shape treatment decisions and patient outcomes. As new therapeutic options emerge, it is critical to consider both the benefits and risks associated with their use. Careful monitoring of the safety profile of tofacitinib remains vital to ensure patient health and minimize side effects.
Although research is ongoing, the need for evidence-based approaches cannot be overstated. Clinicians should stay apprised of developments in the context of tofacitinib and granuloma annulare. This ensures that treatment strategies remain current and effective, benefitting patients who struggle with this condition.
Summary of Findings
The findings presented in this article elucidate the potential role of tofacitinib in managing granuloma annulare. Key points include:
- Efficacy: Data from case studies and clinical trials suggest a positive response to treatment in many patients.
- Safety: While potential side effects exist, they can be effectively monitored and managed.
- Comparison with traditional therapies: Tofacitinib appears to offer advantages over standard treatment options, potentially leading to improved patient outcomes.
These findings create a framework for understanding the intersection of medication and dermatological disease, encouraging further exploration in this realm.
Implications for Clinical Practice
For practitioners, the insights gained from this analysis underscore several important considerations:
- Informed Decision-Making: The efficacy and safety of tofacitinib indicate its relevance as an alternative to more traditional therapies. This can be pivotal when managing granuloma annulare in patients who do not respond to conventional treatments.
- Patient-Centered Care: Understanding the specific characteristics of granuloma annulare and the patient's unique situation allows for tailored treatment plans. Discussing the potential benefits and risks of tofacitinib with patients can empower them in their treatment choices.
- Continued Research: Ongoing studies are essential to further substantiate findings related to tofacitinib and its impact on granuloma annulare. Clinicians should advocate for and participate in research initiatives that enhance knowledge in this area.



